Use of core and common information and technology solutions framework
Purpose
The Use of core and common information and technology solutions policy sets out the requirements for Queensland Government agencies to implement core and common reusable solutions in their digital and ICT asset environments. This framework provides agencies with guidance and processes to demonstrate compliance with the core and common requirements.
What is core and common?
Core and common promotes reuse of information and technology solutions to address business capability needs across government. The scope of applicability of these solutions is defined as follows:
- Core: information and technology solutions that are required by all agencies to function, such as payroll solutions, human resource solutions, finance solutions.
- Common: information and technology solutions that deliver similar services in a subset of agencies, such as grants management solutions, computer-aided emergency dispatch solutions.
This framework relates to core and common reusable information and technology solutions within the whole-of-government context. These include:
- Services: delivery of reusable and centralised capability to support agency outcomes.
- Platforms: foundation capability that creates, deploys, and hosts agency solution instances.
- Enabling technology: technology that augments, supports, and enables platforms and services.
The approach supports the Digital Government priority under the Queensland Digital Economy Strategy and Action Plan. A priority of the strategy and action plan is the identification of business capabilities across agencies that are similar yet are currently supported by different information and technology solutions. In some instances, the solution choices being made are comparable and/or interchangeable and leading to agencies duplicating efforts in their identification, procurement and implementation of information and technology solutions.
Core and common empower agencies in the management of the ICT environment by simplifying decision-making when considering the complex array of solutions available. Through the core and common approach agencies can leverage relevant and timely guidance, empowering agencies to manage and map their current and future ICT state, and plan for any future transition with confidence.
For an information and technology solution to be considered core or common, it must provide collective benefits (i.e. time to value, efficiency, resource utilisation, security, cost, market engagement, etc.) to the sector.
Core and common does not include any information and technology solutions that are specific to agencies’ businesses or do not provide collective benefits.
Alignment to principles
Core and common investments are guided by the broader Digital Investment Governance Framework principles.
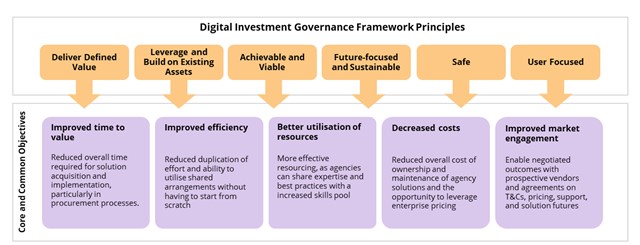
Concept of operations
A core and common solution is more than just the software or hardware product. The concept of operations for the solution must define the way information and technology solutions will be managed as a service offering, including business requirement fit, lifecycle management, governance, and procurement arrangements so that it can become operational as a solution reused across government.
These operational requirements are documented in the concept of operations for the solution and cover the following dimensions.
| Governance | Requirements | Market engagement |
| Funding mechanism | Procurement | Product selection |
| Implementation | Hosting | Instance / tenancy |
| Solution support | Accessibility | Lifecycle management |
Core and common catalogue
Currently mandated and endorsed core and common solutions are listed in the Core and common summary – mandated and endorsed products and are also available from the core and common catalogue. The Core and common catalogue is a central repository that provides visibility of the core and common information and technology solutions that are being investigated and those that are available/in use. The catalogue is published via the Digital Console.
Government employees: If you have issues logging into the Core and common catalogue, go to the Digital console help page for more information.
Due to each agency’s complex services, functions, and contextual differences, there may be no ‘one size fits all’ information and technology solution. As such, the catalogue may list multiple solutions for different thresholds such as agency size and complexity.
Over time, an agency’s ICT environment will likely include a combination of information and technology solutions that are agency-specific or part of the core and common catalogue.
Preliminary core and common review
The catalogue supports an agency conducting a preliminary core and common review when evaluating information and technology solutions investments.
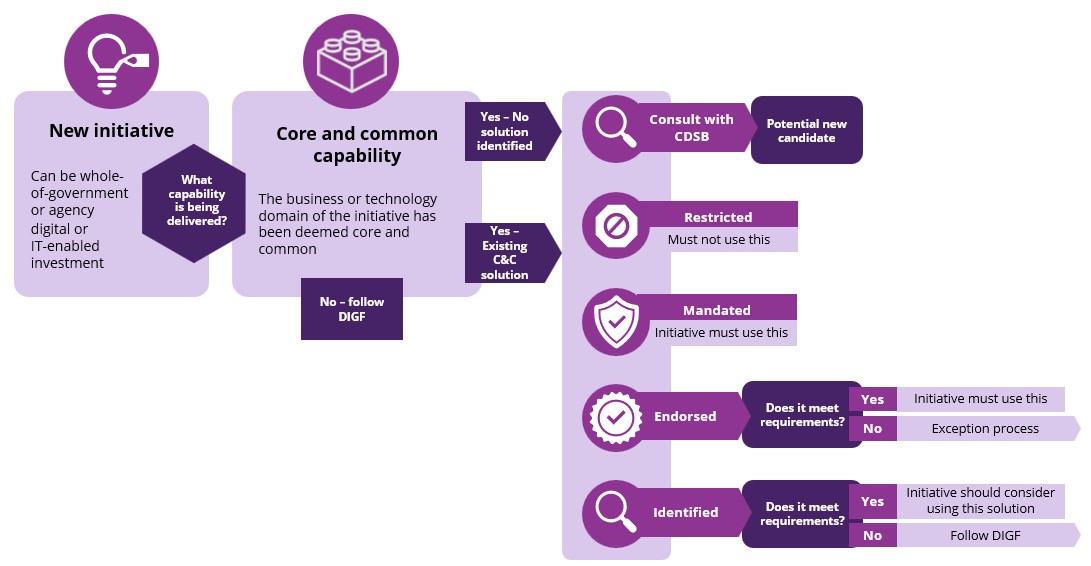
During the review, an agency can use the catalogue for the following:
- find the appropriate capability that the new initiative is delivering
- determine if that capability is deemed core or common
- find any known solutions for that capability and what status they have
- determine which, if any, of these solutions can apply to the initiative
- drill down to further information on how to implement the solution by viewing supporting documentation such as such as procurement instruments and the concept of operations.
Agency portfolio offices and architecture practices should guide initiatives toward conducting this review as early as possible. Initiative owners can self-service from the Core and Common Catalogue or seek assistance from the Office of Assurance and Investment.
Core and common domains without existing solutions
Some domains deemed core and common may not yet have associated solutions. In this instance, an agency initiative within a core and common domain will either:
- consider core and common requirements as part of their activities, engaging with DELSG and CDSB as a solution is identified
- apply for an exception so that their activities do not have to consider core and common requirements for that domain.
CDSB should be engaged early in activities where initiatives are occurring in core and common domains without identified solutions.
Solution status classification
Core and common information and technology solutions listed in the catalogue will have one of the following statuses. The status of a core and common solution will be determined through consultation across the sector and with the Digital Leaders Group and approved by DELSG.
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Mandated | The solution has been deemed as ‘must use’ by Queensland Government. Agencies must adopt this solution. Agencies are responsible for leveraging any whole of government business operating model (e.g., procurement, implementation, licensing, support) for the solution. There is no exception process for alternatives. |
| Endorsed | Agencies are required to adopt this solution. However, a limited exception process exists for alternatives. There will likely be time and / or cost advantages for adopting this solution, or whole of government target architectural alignment. Agencies are responsible for their own due diligence and leveraging any whole of government business operating model (e.g., procurement, implementation, licensing, support) for the solution. |
| Identified | The solution has potential reuse. e.g., due to existing Common Use Supply Arrangements being in place and / or the solution aligns with whole of government target architecture. Agencies are encouraged to investigate this solution first but are free to consider alternatives. However, there will likely be time and / or cost advantages for adopting this solution, or whole of government target architectural alignment. Agencies are responsible for their own due diligence and leveraging any whole of government procurement instruments. |
| Restricted | The solution has been deemed no longer suitable for Queensland Government use. Agencies must plan to migrate to an alternate solution. The urgency of migration will be determined on a case-by-case basis. |
Governance framework
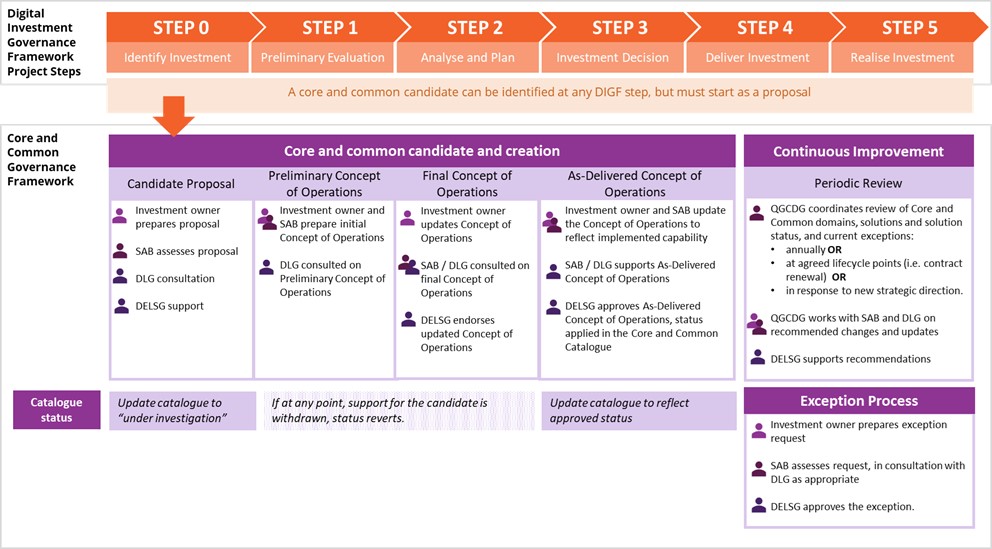
Core and common aligns to and is applied within the Digital Investment Governance Framework (DIGF). Ideally, the preliminary core and common review occurs at Step 0 of the DIGF, but it can occur at any step.
The following roles enable the framework:
| Group involved | Role |
|---|---|
| Office of Investment, Assurance and Architecture | Operates the Digital Investment Governance Framework (DIGF) and monitors the implementation of the core and common governance framework within it |
| Solution Advisory Board (SAB) | A governance body that reports to the Digital Economy Leaders Sub-Groub (DELSG) and provides their assessments on core and common solutions to assist DELSG decision making. The SAB is made up of appropriate agency representatives to ensure solutions meet agency requirements during identification, selection, and prioritisation of core and common candidates. |
| Digital Economy Leaders Sub-Group (DELSG) | The governance body responsible for prioritising core and common capability, endorsing concepts of operations, and approving core and common solutions. |
| Investment owner | The proposer/sponsor of an initiative progressing through the DIGF. |
| Digital Leaders Group (DLG) | The CIOs, CTOs, and CDOs from across the sector. |
The processes within the Core and common governance framework (Appendix A) are intended to use templates and steps from existing initiative and project methods. This makes it easier to achieve core and common objectives without being an overhead on initiative and investment progression.
Core and common candidate and creation
This process follows the proposal, development, and introduction of a new core and common solution.
- Initial proposal
- If an investment owner or CDSB deems a solution should be considered as a candidate for inclusion within core and common they can complete a proposal for submission to the Solution Advisory Board (SAB). The proposal will detail the business need and capability the proposed solution addresses and how it compares to any pre-existing Core and Common solutions.
- The SAB will review the proposal and undertake consultation with the Digital Leaders Group (DLG). After consultation, the SAB will submit to DELSG an assessment report that will set out whether they endorse inclusion into core and common or not. The assessment provided by the SAB will consider various factors including agency requirements, feasibility, and current domain solutions. Regardless of the recommendation of the SAB report it will, along with the original business proposal, progress to DELSG for review.
- Preliminary concept of operations
- If DELSG supports the candidate, the investment owner will work with the SAB (and SMEs as required) to complete a preliminary concept of operations.
- The SAB will consult with the DLG regarding the preliminary concept of operations to DELSG.
- Final concept of operations
- The investment owner updates the preliminary concept of operations following consultation.
- The SAB and DLG will be consulted on the final concept of operations.
- DELSG will endorse the final concept of operations.
- As-delivered concept of operations
- When the investment has been delivered, and the solution is enabled, the investment owner and the SAB will update the concept of operations as required to match as-delivered solution.
- Support of the As-Delivered Concept of operations will be sought from SAB and DLG.
- DELSG endorses this version of concept of operations, assigns a status to the solution, and endorses the entry in the Core and common catalogue.
Core and common exception process
This process follows the application for departure from adopting an endorsed core and common solution.
- The investment owner will complete an exception request (QGEA exception guideline) which describes the capability domain the proposed solution addresses. The request should make clear any ‘endorsed’ solutions that currently cover the capability or domain and provide a detailed rationale why the endorsed solutions are not fit for purpose.
- The SAB will assess the request and consults with DLG as appropriate. The SAB will consider if:
- the proposed investment should be assessed as a new core and common solution for the domain, or if the new solution could address the limitations of an existing endorsed solution and potentially replace it
- the investment is seeking specialised capability and therefore does not fall under the core and common solutions in that domain.
- The SAB will make a recommend to DELSG regarding the exception.
- DELSG will approve the exception.
Core and common continuous improvement
- Core and common solutions will be periodically reviewed and if assessed as no longer suitable, a requirements-based approach will revisit the concept of operations. Some timeline events that might trigger this review are renewal of contract or product retirement.
- Core and common capability coverage will be reviewed and compared with priority of strategic direction, or upcoming programs of work. Based on these factors, the SAB can recommend a new candidate proposal for a capability area without coverage.
- The exceptions log will be reviewed and if a capability has an increasing number of exceptions, the SAB can recommend a candidate proposal to address the limitations of the existing endorsed solution/s.
- In all the cases above, DELSG support is required to initiate the candidate process.